Overview
The first step of processing AP workloads is load the basic full data into rapid engine, then rapid will start propagation operation automatically. When a table loaded from innodb to rapid engine, some meta informations will be also loaded into catalog table, such as performance_schema.rpd_column, performance_schema.rpd_column_id, etc. A backgroud thread will be launched when system start, then start to monitor the redo log, when a new DML operation done, this background thread starts to parse the incoming redo log, and apply the changes into IMCS.
When the load statement was executed, it would peform the load operation. Overall, just like insert into xxx select xxx statement, the system firstly do a table scan via index or full table scan.
1: It scans the target table, usually it is an innodb table. And, here, there is a problem must be clarified at first. That is which data will be visible to operation, and which is not. Therefore, here, we define that only the committed data will be visible to scan operation. In other words, that means we will use auto commited transaction to do table scan. the transaciton will be read committed isolation level. The new data inserted when we do table scaning, all these the latest data will not be seen by the operation, because this would not happen. An exclusive mdl lock is used to protected the new rows are inserted into table when the loading operation is running.
2: Except the core functions, there must be some system parameters to monitors the load operations, for example, how many data have been loaded? and how many remains, and so on. some parallel related parameters also will be introduced into, such as POD( parallel of degree), etc. Therefore, some system parameters will be introduced..
Column Data Format
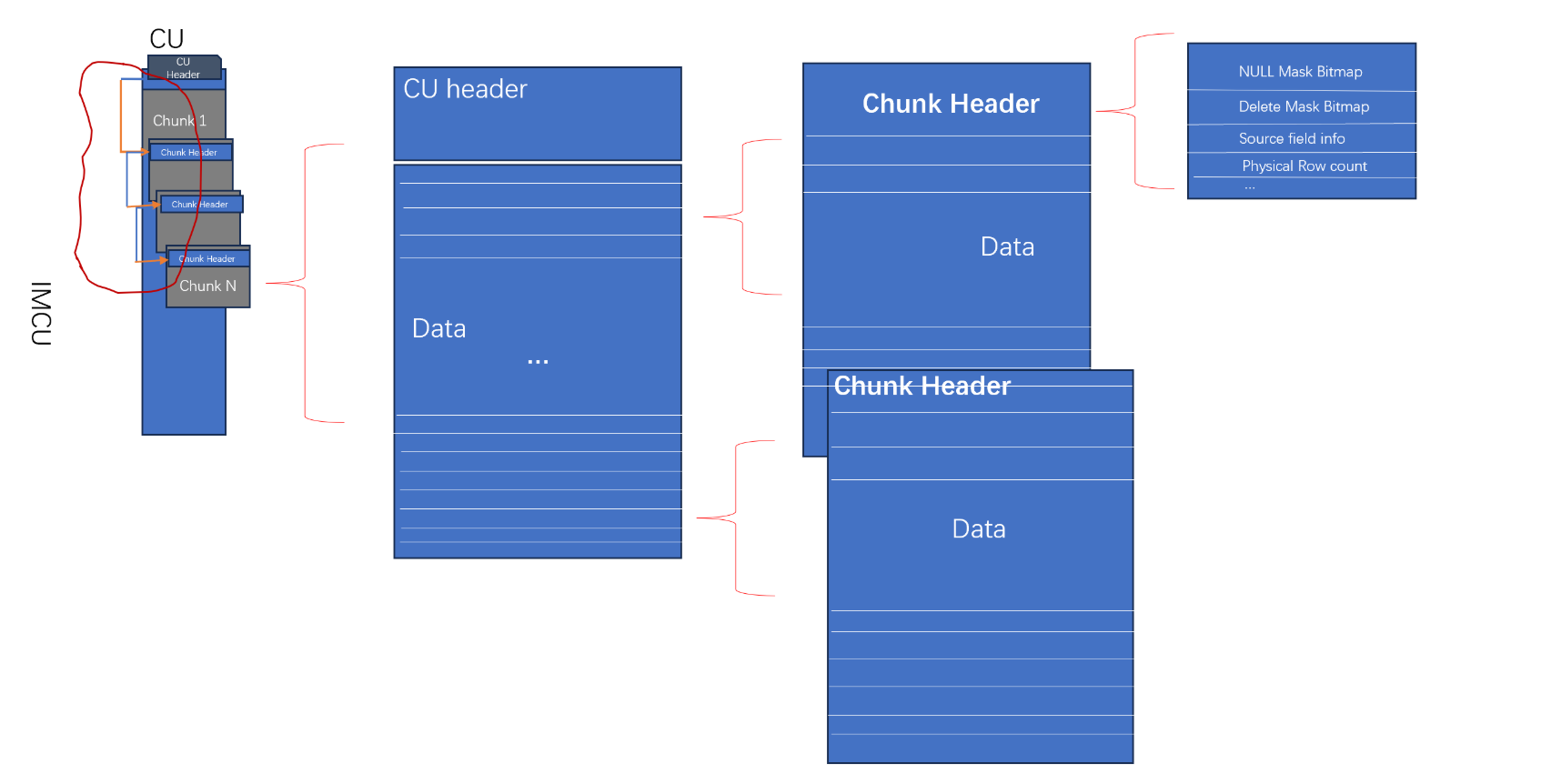
Each column is organized as a file, when it flushes to disk. The format of columns in memory is also called as IMCU(In-memory column unit). An IMCU consisted by CUs(Column Unit), A CU has two parts: (1) Header, Meta Information; (2) Data; Data also can be divided into a bunch of chunks. Each chunk has 122880 rows data, which is same as DuckDB's.
All chunks are linked. The address of the first chunk can be found from Cu's header, and also contains the address of the next chunk. A chunk's consist with header and data. Header contains the meta information of this chunk. the data part is where the real data located. Gets the first Cu from IMCS. In an IMCS instance header, it has a header, which has a pointer to the address of IMCU. When a new data in, it stores it in order. Insert sort can be used to make it ordered. It uses binary search to find the data. But it data is in compressed format, at this situation, we need a new algorithm to find the data in compresssed data. Now, we go to deeper. Giving out the more specific details of the data. Here, we notice that every data we write into CU should a tansaction id attached to it to mark which transaction it belongs.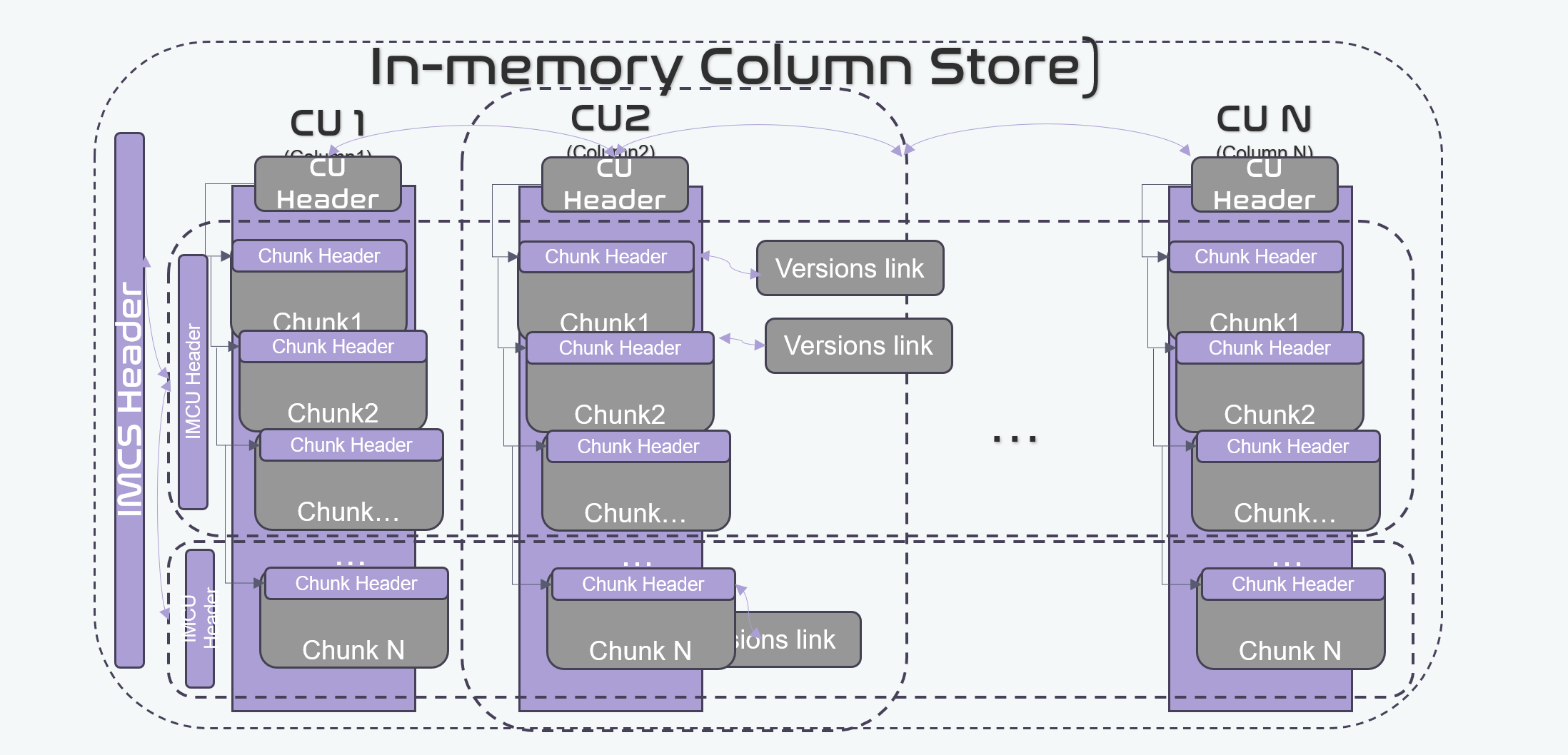
All the variable length data, such as text, string, etc. are encoded into a double tyep in its local dictionary. Each one has a double typed id when it loaded into rapid.
IMCS
In Memory Column Store, IMCS. Singleton pattern, Only ONE instance in rapid engin. It used to represent an in-memory store instance. we can use it to perform full table scan or index table scan to getting the data from it. It has several IMCUs, An IMCU has some Chunks.
Table
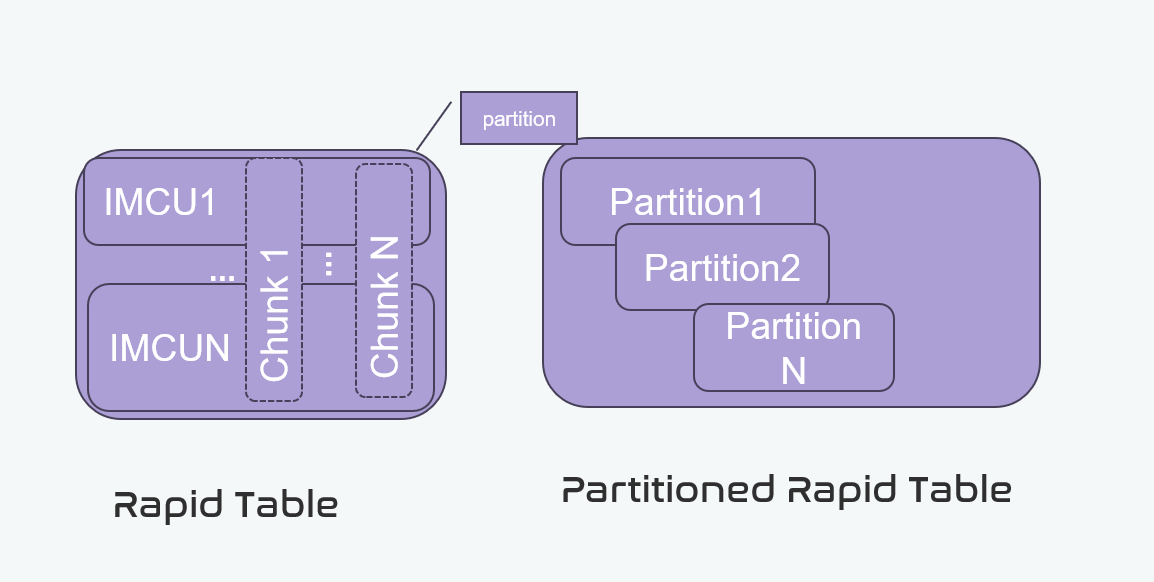
A table is consisted by several columns. Each column is represented by an IMCU in IMCS. When a table is loaded into rapid engine, each column will be created an IMCU instance in IMCS. The meta information of the table is stored in catalog table, such as performance_schema.rpd_column, performance_schema.rpd_column_id, etc. If a table is partitioned table, each partition is also a table. Each partition will be created an IMCS instance in rapid engine.